注意:本 Spring Boot 系列文章基于 Spring Boot 版本 v2.1.1.RELEASE 进行学习分析,版本不同可能会有细微差别。
前言
不管是通过官方提供的方式获取 Spring Boot 项目,还是通过 IDEA 快速的创建 Spring Boot 项目,我们都会发现在 resource 有一个配置文件 application.properties,也有可能是application.yml.这个文件也就是 Spring Boot 的配置文件。
1. YAML 文件
在 Spring Boot 中,官方推荐使用 properties 或者 YAML 文件来完成配置,对于 YAML 文件格式还不了解的可以查看官方的具体格式,这里只做简单介绍。
YAML 语法规则:
- 大小写敏感
- 缩进表示层级
- 缩进只能使用空格
- 空格的数量不重要,但是相同层级的元素要左侧对齐
#开头的行表示注释
YAML 支持的数据结构:
-
单纯的变量,不可再分的单个的值,如数字,字符串等。
name: Darcy age: 12 # ~表示NULL值 email: ~ # 多行字符串可以使用|保留换行符,也可以使用>折叠换行。 # +表示保留文字块末尾的换行,-表示删除字符串末尾的换行。 message:|- Hello world -
数组,一组按次序排列的值。
lang: - java - golang - c # 或者行内写法 lang:[java,golang,c] -
对象,键值对的集合。
person: name:Darcy age:20 # 或者行内写法 person:{name:Darcy,age:20}
使用 YAML 支持的三种数据结构通过组合可以形成复杂的复合结构。
# 服务启动端口号
server:
port: 8080
# 配置person属性值
person:
last-name: Darcy
age: 20
birth: 2018/01/01
email: [email protected]
maps:
key1:java
key2:golang
lists:
- a
- b
- c
dog:
name: 旺财
age: 2
需要注意的是 YAML 文件不能使用@PropertySource 加载
2. Properties 文件
properties 配置文件简单好用,在各种配置环境里都可以看到它的身影,它简单易用,但是在配置复杂结构时不如 YAML 优雅美观。同样拿上面的 YAML 的复合结构举例,演示同样的配置在 properties 文件中的写法。
# 服务启动端口号
server.port=8080
# 配置属性值(使用IDE进行配置需要处理编码问题,不然中文会发送乱码现象)
person.last-name=张三
person.age=18
person.birth=2018/12/06
[email protected]
person.maps.key1=c
person.maps.key2=java
person.maps.key3=golang
person.lists=a,b,c,d
person.dog.name=旺财
person.dog.age=1
3. 随机数与占位符
RandomValuePropertySource 类对于注入随机值很有用(例如,注入秘密或测试用例)。它可以生成整数,长整数,uuid 或字符串等,通过 Spring Boot 对我们的封装,我们可以轻松的使用。
占位符允许在配置的值中引用之前定义过的变量。
# 生成随机值
bootapp.secret=$ {random.value}
bootapp.number=$ {random.int}
bootapp.bignumber=$ {random.long}
bootapp.uuid=$ {random.uuid}
bootapp.number.less.than.ten=$ {random.int(10)}
bootapp.number.in.range=$ {random.int [1024,65536]}
# 属性的占位符
bootapp.name=SpringBoot
bootapp.description=${bootapp.name}是一个spring应用程序
4. 配置的使用
通过上面的介绍,可以发现不管是使用 YAML 还是 Properties 都可以进行配置文件的编写,但是还不知道具体的使用方式,通过下面的几个注解,可以让我们了解到这些配置的具体使用方式。
在使用配置之前,添加所需依赖。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- 导入配置文件处理器,在配置相关文件时候会有提示 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
4.1 ConfigurationProperties
@ConfigurationProperties 注解是 Spring Boot 提供的一种使用属性的注入方法。不仅可以方便的把配置文件中的属性值与所注解类绑定,还支持松散绑定,JSR-303 数据校验等功能。以上面演示的 Properties 的配置为例演示 @ConfigurationProperties 注解的使用。
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import javax.validation.constraints.Email;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* <p>
* @Author niujinpeng
* @Date 2018/12/6 22:54
*/
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated
public class Person {
private String lastName;
private Integer age;
private Date birth;
private Map<String, String> maps;
private List<String> lists;
private Dog dog;
/**
* 支持数据校验
*/
@Email
private String email;
}
@Data是 Lombok 的注解,会为这个类所有属性添加 getting 和 setting 方法,此外还提供了equals、canEqual、hashCode、toString 方法。@Component自动添加 bean 到 spring 容器中。@ConfigurationProperties告诉这个类的属性都是配置文件里的属性,prefix 指定读取配置文件的前缀。
4.2 Value
@Value 支持直接从配置文件中读取值,同时支持 SpEL 表达式,但是不支持复杂数据类型和数据验证,下面是具体的使用。
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import javax.validation.constraints.Email;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Data
@Component
@Validated
public class PersonValue {
/**
* 直接从配置文件读取一个值
*/
@Value("${person.last-name}")
private String lastName;
/**
* 支持SpEL表达式
*/
@Value("#{11*4/2}")
private Integer age;
@Value("${person.birth}")
private Date birth;
/**
* 不支持复杂类型
*/
private Map<String, String> maps;
private List<String> lists;
private Dog dog;
/**
* 不支持数据校验
*/
@Email
@Value("xxx@@@@")
private String email;
}
编写单元测试代码测试代码查看属性绑定是否成功。
import net.codingme.boot.domain.Person;
import net.codingme.boot.domain.PersonValue;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class HelloApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mvc;
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Autowired
private PersonValue personValue;
/**
* 模拟请求测试
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testGetHello() throws Exception {
mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string("Greetings from Spring Boot!"));
}
/**
* 测试@ConfigurationProperties
*/
@Test
public void testPersion() {
System.out.println(person);
}
/**
* 测试@Value 引入配置值
*/
@Test
public void testPersionValue() {
System.out.println(personValue);
}
}
运行发现数据已经正常绑定。
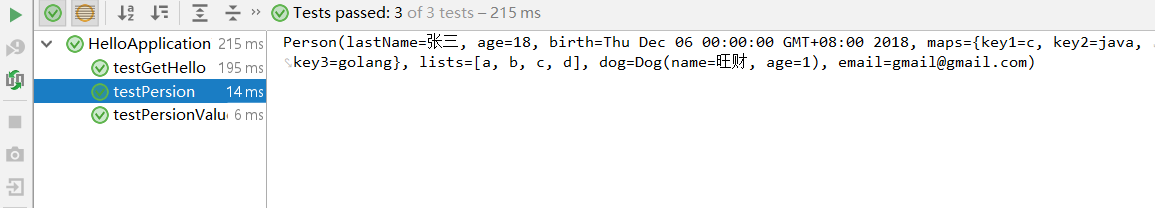
通过上面的示例,也可以发现 @ConfigurationProperties 和 @Value的区别。
| 特征 | @ConfigurationProperties | @Value |
|---|---|---|
| 功能 | 批量注入配置文件属性 | 一个一个注入 |
| 松散绑定(松散的语法) | 支持 | 不支持 |
| SpEL | 不支持 | 支持 |
| JSR-303 数据校验 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 复杂类型 | 支持 | 不支持 |
@ConfigurationProperties 和 @Value的使用场景。
如果说,只是在某个业务逻辑中获取配置文件的某个值,使用 @Value.
如果说,专门编写有一个 Java Bean 来和配置文件映射,使用 @ConfigurationProperties.
4.3 PropertySource
随着业务复杂性的增加,配置文件也越来越多,我们会觉得所有的配置都写在一个 properties 文件会使配置显得繁杂不利于管理,因此希望可以把映射属性类的配置单独的抽取出来。由于 Spring Boot 默认读取 application.properties,因此在抽取之后之前单独的@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")已经无法读取到信息。这是可以使用 @PropertySource 注解来指定要读取的配置文件。
需要注意的是,使用 @PropertySource 加载自定义的配置文件,,由于 @PropertySource 指定的文件会优先加载,所以如果在 applocation.properties 中存在相同的属性配置,会覆盖前者中对于的值。
如果抽取 person 配置为单独文件domain-person.properties。
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import javax.validation.constraints.Email;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* <p>
* @Author niujinpeng
* @Date 2018/12/6 22:54
*/
@Data
@Component
@Validated
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:domain-person.properties")
@ConfigurationProperties(value = "person")
public class PersonSource {
private String lastName;
private Integer age;
private Date birth;
private Map<String, String> maps;
private List<String> lists;
private Dog dog;
/**
* 支持数据校验
*/
@Email
private String email;
}
5. 多环境配置
在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{name}.properties.默认使用的是application.properties.
5.1 properties 多环境
那么如何在配置文件中激活其他的配置文件呢?只需要在 application.properties 启用其他文件。
# 激活 application-prod.properties文件
spring.profiles.active=prod
5.2 YAML 多环境
如果是使用 YAML 配置文件,我们可以使用文件块的形式,在一个 YAML 文件就可以达到多文件配置的效果,下面是 Spring Boot 使用 YAML 文件进行多环境配置的方式。
server:
port: 8083
profiles:
active: dev # 指定环境为dev
# 使用三个---进行文档块区分
---
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8085
spring:
profiles: prod
5.3 多环境激活方式
除了以上的两种配置文件激活方式之外,还有另外两种种激活方式。
- 命令行 ,运行时添加
--spring.profiles.active=prod - Jvm 参数 ,运行时添加
-Dspring.profiles.active=prod
如果需要激活其他的配置文件,可以使用 spring.config.location=G:/application.properties 进行配置。
6. 配置文件加载顺序
配置文件默认会从四个地方加载,且优先级从高到低。优先级高的配置会覆盖优先级低的配置。如果多个位置的配置同时存在,不同的配置信息会形成互补配置。
-file: ./config/
-file: ./
-classpath: /config/
-classpath: /
7. 外部配置文件
Spring Boot 的外部配置文件加载的方式有很多,具体可以参考官方文档。这些配置加载优先级从高到底,优先级高的配置会覆盖优先级低的配置。
下面介绍几种常见的加载配置的顺序。
- 命令行参数运行,所有的配置都可以在命令行上执行,多个配置空格隔开。
java -jar springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=9999 --sercer.context-path=/spring
- jar 包目录下的 application-{profile}.properties (或yml)文件
- jar 包里的 application-{profile}.properties (或yml)文件
- jar 包目录下的 application.properties (或yml)文件
- jar 包里下的 application.properties (或yml)文件
文章代码已经上传到 GitHub Spring Boot 配置文件。